PCB Editor
Enhanced Metal Density Scan
- All Allegro X Tiers
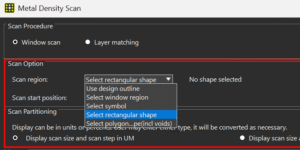 The metal density scan has been enhanced with polygon-based region selection which also supports voids. To improve usability, scan region labels now specify the shape type, rectangular or polygonal, and related option names are clearer.
The metal density scan has been enhanced with polygon-based region selection which also supports voids. To improve usability, scan region labels now specify the shape type, rectangular or polygonal, and related option names are clearer.
Copy and Paste Layout
- All OrCAD X Tiers
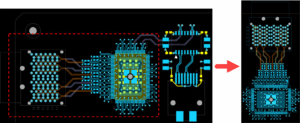 Simplify design reusing by replacing file-based methods and place replicate methods with a direct clipboard-based workflow. You can now copy placement, routing, vias, and shapes between designs without intermediate files, saving time and accelerating design cycles. This method includes intelligent mapping for a seamless transition. Upon pasting, a dialog box guides you through the correct integration of the copied layout into the target design.
Simplify design reusing by replacing file-based methods and place replicate methods with a direct clipboard-based workflow. You can now copy placement, routing, vias, and shapes between designs without intermediate files, saving time and accelerating design cycles. This method includes intelligent mapping for a seamless transition. Upon pasting, a dialog box guides you through the correct integration of the copied layout into the target design.
Status Command Dialog Box
- All OrCAD X Tiers
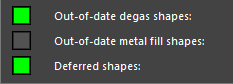 The status command dialog box has been updated with new fields, providing enhanced visibility and control over the status of design shapes. This includes:
The status command dialog box has been updated with new fields, providing enhanced visibility and control over the status of design shapes. This includes:
- Degas shapes: Reports the number of out-of-date degas shapes and provides an Update Degas option.
- Metal Fill Shapes: Reports the number of out-of-date metal fill shapes and provides an Update Metal Fill option.
- Deferred Shapes: Reports the number of deferred shapes and provides a Defer All Off option.
Performance Enhancements
- All OrCAD X Tiers
Cadence is committed to continuous improvement of the performance of its products, which, in turn, impacts your productivity. Performance enhancements are included for design synchronization, DFA, Find by Query, placement and interactive placement for modules, via arrays and via structures, net loop report, routing and interactive routing and more.
SKILL Enhancements
- All OrCAD X Tiers
The following new SKILL functions have been added:
- axl3DXGetDesignOption: Returns the value of a 3DX design option for the current design database
- axl3DXSetDesignOption: Modifies the value of a 3DX design option for the current design database.
- axlShapeFreezeAll: Identifies all dynamic shapes in the design that are not frozen and sets their status to frozen.
- axlShapeIsFrozen: Checks whether a given dynamic shape is frozen, returns nil if the shape is not dynamic.
- axlShaeSetFrozen: Identifies the list of provided shapes and updates their frozen status based on the specified status flag.
- axlShapeUnfreezeAll: Locates all frozen dynamic shapes in the design and changes their status to unfrozen.
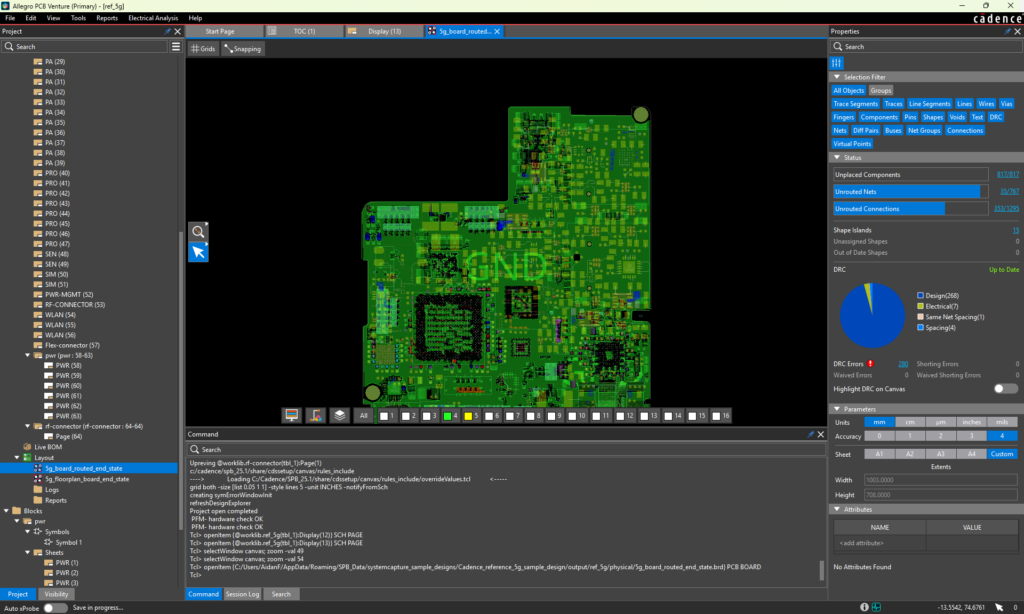
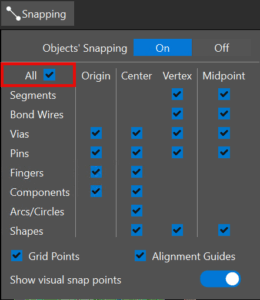 Snapping control has been enhanced and snapping configuration simplified. A new keyboard shortcut has been added to toggle snapping and snapping cursor display without leaving the layout editor, reducing workflow interruptions. A new All check box to activate snapping for all objects has been added, streamlining snapping configuration.
Snapping control has been enhanced and snapping configuration simplified. A new keyboard shortcut has been added to toggle snapping and snapping cursor display without leaving the layout editor, reducing workflow interruptions. A new All check box to activate snapping for all objects has been added, streamlining snapping configuration. With this release, OrCAD X Presto introduces the ability to perform instant fanout on multiple pins. Draw a window around a group of pins to select them to perform the instant fanout.
With this release, OrCAD X Presto introduces the ability to perform instant fanout on multiple pins. Draw a window around a group of pins to select them to perform the instant fanout.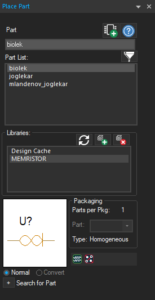 PSpice now supports advanced built-in functions to model memristors. The new models are included in the memristor.olb library.
PSpice now supports advanced built-in functions to model memristors. The new models are included in the memristor.olb library.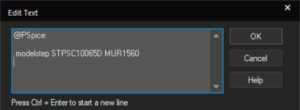 PSpice now supports sweeping of components models to perform design exploration with different models in a single simulation run. Evaluate different models for a given base model and compare them to see how the circuit behavior changes for different models.
PSpice now supports sweeping of components models to perform design exploration with different models in a single simulation run. Evaluate different models for a given base model and compare them to see how the circuit behavior changes for different models.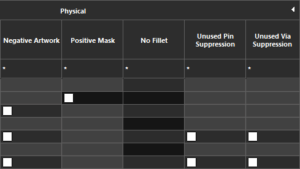 This release introduces positive masks, an enhancement for mask layer visualization and manufacturability. Traditionally, mask layers are negative, where the visible objects on the canvas represent openings in the mask. The traditional approach requires designers to mentally invert the image to understand the manufactured outcome. Interpreting these negative mask visuals as positive during 3D rendering or manufacturability checks can be counterintuitive and error-prone, adding complexity to the design and review process.
This release introduces positive masks, an enhancement for mask layer visualization and manufacturability. Traditionally, mask layers are negative, where the visible objects on the canvas represent openings in the mask. The traditional approach requires designers to mentally invert the image to understand the manufactured outcome. Interpreting these negative mask visuals as positive during 3D rendering or manufacturability checks can be counterintuitive and error-prone, adding complexity to the design and review process.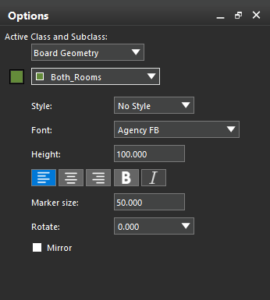 This update modernizes the way text is managed in PCB designs, aligning the tool with industry-standard applications. You now have the flexibility to choose from a wide range of fonts that reflect personal or corporate branding while also improving the visual clarity and consistency of design documentation. In addition to standard fonts, the Mooretronics font is also supported within layout editors.
This update modernizes the way text is managed in PCB designs, aligning the tool with industry-standard applications. You now have the flexibility to choose from a wide range of fonts that reflect personal or corporate branding while also improving the visual clarity and consistency of design documentation. In addition to standard fonts, the Mooretronics font is also supported within layout editors.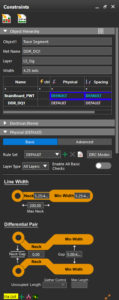 The docked Constraint Manager is a new Constraints panel that simplifies the process of assigning and visualizing constraints directly from the Layout Editor user interface. It presents constraints in a graphical format and organizes them under Basic and Advanced modes. Constraints can be controlled at the group level rather than the net level by assigning constraint sets at the net group, net class, and differential pair levels within the Object Hierarchy panel.
The docked Constraint Manager is a new Constraints panel that simplifies the process of assigning and visualizing constraints directly from the Layout Editor user interface. It presents constraints in a graphical format and organizes them under Basic and Advanced modes. Constraints can be controlled at the group level rather than the net level by assigning constraint sets at the net group, net class, and differential pair levels within the Object Hierarchy panel.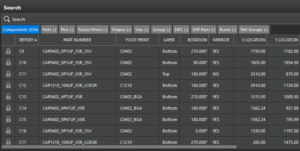 The Search panel is a new dockable panel that allows you to instantly query database objects and cross-probe them from the canvas or panel to find information and objects quickly. This provides on-demand content loading to reduce memory usage and improve performance, real-time updates to ensure you have access to the latest information, and custom column filtering to allow columns to be rearranged as needed.
The Search panel is a new dockable panel that allows you to instantly query database objects and cross-probe them from the canvas or panel to find information and objects quickly. This provides on-demand content loading to reduce memory usage and improve performance, real-time updates to ensure you have access to the latest information, and custom column filtering to allow columns to be rearranged as needed.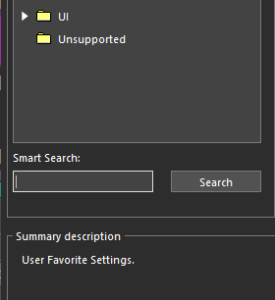 Smart Search is a new search engine that generates predictions based on entered keywords or questions to find the information you need to complete a task directly in the layout. This feature is useful when modifying the design by applying object properties or setting user preferences while working on it.
Smart Search is a new search engine that generates predictions based on entered keywords or questions to find the information you need to complete a task directly in the layout. This feature is useful when modifying the design by applying object properties or setting user preferences while working on it.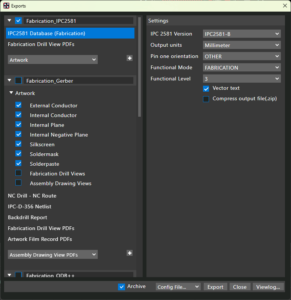 A new configuration-based solution defines all required data exports and manages export parameters in a single dialog box. It eliminates the need to explore different areas of the layout editor to produce manufacturing exports.
A new configuration-based solution defines all required data exports and manages export parameters in a single dialog box. It eliminates the need to explore different areas of the layout editor to produce manufacturing exports.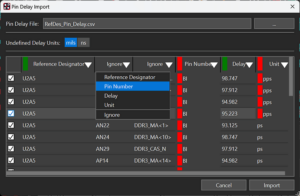 The enhanced pin delay import feature provides auto-detection, column and cell validation, and the ability to adjust column categories and values directly within the dialog box without modifying the source CSV file. The enhanced functionality queries the database to flag missing Reference Designator and Pin Number combinations in the design and allows selective import by deactivating rows and columns as required.
The enhanced pin delay import feature provides auto-detection, column and cell validation, and the ability to adjust column categories and values directly within the dialog box without modifying the source CSV file. The enhanced functionality queries the database to flag missing Reference Designator and Pin Number combinations in the design and allows selective import by deactivating rows and columns as required.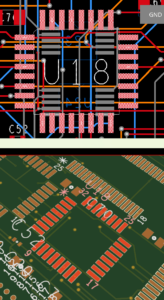 In this release, Cadence continues to expand the capabilities of 3DX Canvas, helping designers visualize their PCB layouts in a highly realistic 3D environment before sending the layouts to manufacturing. 3DX Canvas has been enhanced to selectively display and incrementally add objects to the 3DX Canvas, making the environment far more interactive and efficient. You can now highlight selected objects in the 3DX canvas from the PCB, cross-probe objects, and adjust the 3D view automatically.
In this release, Cadence continues to expand the capabilities of 3DX Canvas, helping designers visualize their PCB layouts in a highly realistic 3D environment before sending the layouts to manufacturing. 3DX Canvas has been enhanced to selectively display and incrementally add objects to the 3DX Canvas, making the environment far more interactive and efficient. You can now highlight selected objects in the 3DX canvas from the PCB, cross-probe objects, and adjust the 3D view automatically. OrCAD X PCB Editor has several performance enhancements added included DRCs, import and export of design data, placement and interactive placement, routing and interactive routing, dynamic shapes, padstack refresh, 3D view, and in-design analysis.
OrCAD X PCB Editor has several performance enhancements added included DRCs, import and export of design data, placement and interactive placement, routing and interactive routing, dynamic shapes, padstack refresh, 3D view, and in-design analysis.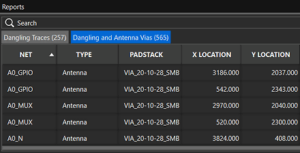 The Reports panel is a new dockable panel that automatically loads selected Quick Reports for easier review and canvas navigation. This panel eliminates the need to manage a separate floating report viewer for the Shape Islands Report, Unassigned Shapes Report, Missing Teardrops Report, Missing Tapers Report, and the Dangling Traces, Vias, and Antenna report.
The Reports panel is a new dockable panel that automatically loads selected Quick Reports for easier review and canvas navigation. This panel eliminates the need to manage a separate floating report viewer for the Shape Islands Report, Unassigned Shapes Report, Missing Teardrops Report, Missing Tapers Report, and the Dangling Traces, Vias, and Antenna report.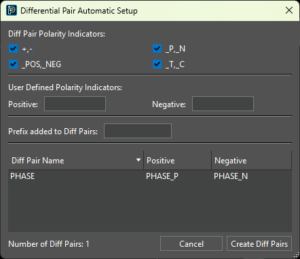 25.1 introduces a new dialog box, Differential Pair Automatic Setup, which provides a unified solution for generating differential pairs. This dialog box combines all unique features in the existing solutions available within and outside the Constraint Manager and simplifies the process of generating differential pairs.
25.1 introduces a new dialog box, Differential Pair Automatic Setup, which provides a unified solution for generating differential pairs. This dialog box combines all unique features in the existing solutions available within and outside the Constraint Manager and simplifies the process of generating differential pairs.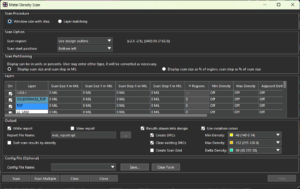 The metal density scan command, used to perform metal density analysis of design layers, is enhanced for performance. The command also provides additional metal density checks and options to meet manufacturing requirements such as minimum/maximum metal density across layers and metal density difference between two layers.
The metal density scan command, used to perform metal density analysis of design layers, is enhanced for performance. The command also provides additional metal density checks and options to meet manufacturing requirements such as minimum/maximum metal density across layers and metal density difference between two layers.
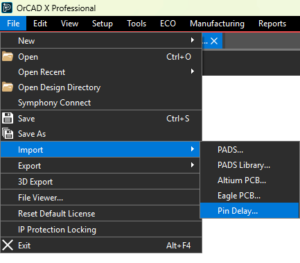 The Import Pin Delay feature allows pin delay to be imported from various file formats, such as Excel files, Allegro Constraint compiler files, and existing pin delay formats.
The Import Pin Delay feature allows pin delay to be imported from various file formats, such as Excel files, Allegro Constraint compiler files, and existing pin delay formats.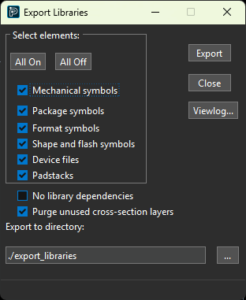 The Export Libraries feature extracts libraries from translated third-party designs, making it easier to reuse libraries in OrCAD X Presto designs.
The Export Libraries feature extracts libraries from translated third-party designs, making it easier to reuse libraries in OrCAD X Presto designs.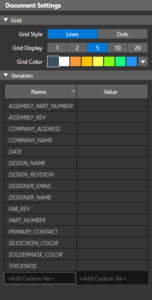 LiveDoc now provides the ability to add assembly notes and instructions as well as using variables in title blocks and assembly notes. The variable values can be defined in the Property panel of LiveDoc and update globally across the document.
LiveDoc now provides the ability to add assembly notes and instructions as well as using variables in title blocks and assembly notes. The variable values can be defined in the Property panel of LiveDoc and update globally across the document.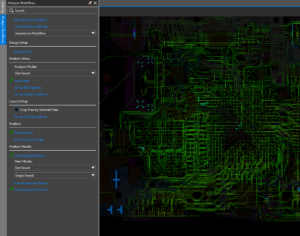
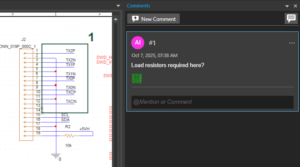 Review a schematic design using comments and markups. Mark any area in the design canvas using rectangular or arrow markups and add text comments in for efficient design reviews.
Review a schematic design using comments and markups. Mark any area in the design canvas using rectangular or arrow markups and add text comments in for efficient design reviews.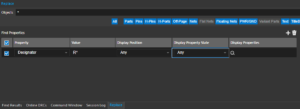 Find objects by parts, pins, nets, text, class, with additional search criteria for object properties and display properties. Efficiently replace values using the new replace dialog box.
Find objects by parts, pins, nets, text, class, with additional search criteria for object properties and display properties. Efficiently replace values using the new replace dialog box.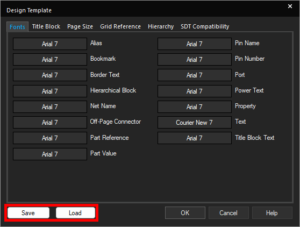 The settings of a design template can now be saved as a .dtp file and loaded to reuse in a design. Save and load templates for later reuse in schematic designs allowing you to quickly configure design properties such as text font and size.
The settings of a design template can now be saved as a .dtp file and loaded to reuse in a design. Save and load templates for later reuse in schematic designs allowing you to quickly configure design properties such as text font and size.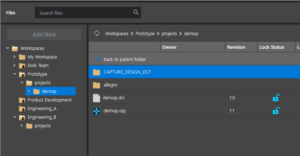 Share workspaces directly via the Web, making collaboration with team members and stakeholders easier. This feature enables seamless sharing of design data, eliminating the need for manual file transfers and ensuring that everyone has access to the latest design information.
Share workspaces directly via the Web, making collaboration with team members and stakeholders easier. This feature enables seamless sharing of design data, eliminating the need for manual file transfers and ensuring that everyone has access to the latest design information.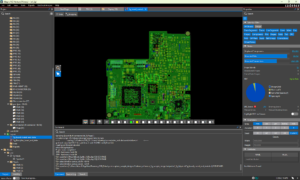 With this unified cockpit designers can seamlessly edit, plan, and modify the PCB layout with the easy-to-use X Layout platform directly in System Capture. This change enhances collaboration between the schematic and PCB layout and incorporates additional features such as preferences and constraints to help communicate design intent upfront.
With this unified cockpit designers can seamlessly edit, plan, and modify the PCB layout with the easy-to-use X Layout platform directly in System Capture. This change enhances collaboration between the schematic and PCB layout and incorporates additional features such as preferences and constraints to help communicate design intent upfront.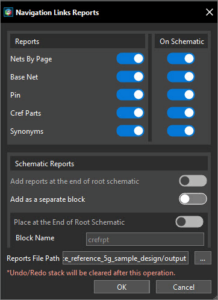 System Capture now supports generating navigation link reports, also called cross-references or CRef reports. Reports for Nets by Page, Base Net, Pin Cross-References, CRef parts, and Synonyms can now be created to be viewed in the schematic or exported as text files. These reports provide detailed connectivity and component cross-referencing insights to help quickly analyze design relationships and locate elements across pages and blocks.
System Capture now supports generating navigation link reports, also called cross-references or CRef reports. Reports for Nets by Page, Base Net, Pin Cross-References, CRef parts, and Synonyms can now be created to be viewed in the schematic or exported as text files. These reports provide detailed connectivity and component cross-referencing insights to help quickly analyze design relationships and locate elements across pages and blocks.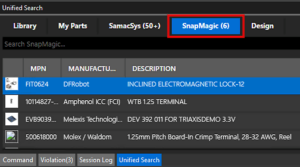 SnapMagic is now available in Unified Search to expand the list of available components. The SnapMagic parts database can be accessed without leaving System Capture.
SnapMagic is now available in Unified Search to expand the list of available components. The SnapMagic parts database can be accessed without leaving System Capture.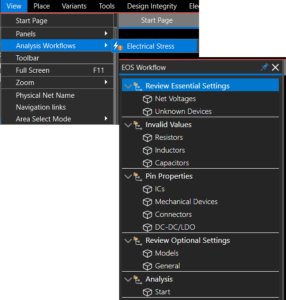 A new workflow to streamline electrical stress analysis has been introduced. The EOS workflow can be accessed under View > Analysis Workflows > Electrical Stress.
A new workflow to streamline electrical stress analysis has been introduced. The EOS workflow can be accessed under View > Analysis Workflows > Electrical Stress.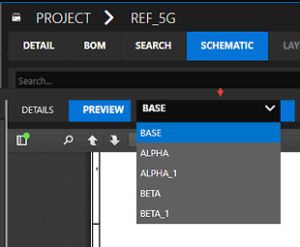 The Pulse web dashboard now supports design variants. To choose a variant, open the Schematic tab and select the Variant dropdown. This enhancement allows designers to switch between variants and easily review or download them.
The Pulse web dashboard now supports design variants. To choose a variant, open the Schematic tab and select the Variant dropdown. This enhancement allows designers to switch between variants and easily review or download them.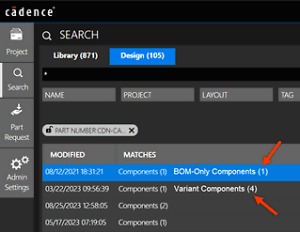 System Capture and the Pulse web dashboard have enhanced design search and version control capabilities. These include:
System Capture and the Pulse web dashboard have enhanced design search and version control capabilities. These include: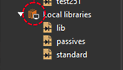 With the new Local Library feature, create and manage libraries directly on your computer. With this new feature, a pulse server connection is not required, all symbols are edited and stored locally with complete formatting support. Anyone can author these local libraries and no role-based restrictions apply. Additionally, custom shapes from managed libraries can be reused and importing pin lists for faster symbol creation is available.
With the new Local Library feature, create and manage libraries directly on your computer. With this new feature, a pulse server connection is not required, all symbols are edited and stored locally with complete formatting support. Anyone can author these local libraries and no role-based restrictions apply. Additionally, custom shapes from managed libraries can be reused and importing pin lists for faster symbol creation is available.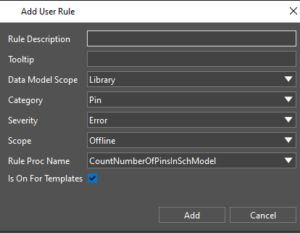 Validation rules now offer enhanced customization for system-defined rules, with the ability to specify the object stages in which they run, such as Validate, Check-in, Pre-Release, and Release. User-defined rules can now be created for all library object types, beyond libraries, parts, symbols, and footprints.
Validation rules now offer enhanced customization for system-defined rules, with the ability to specify the object stages in which they run, such as Validate, Check-in, Pre-Release, and Release. User-defined rules can now be created for all library object types, beyond libraries, parts, symbols, and footprints.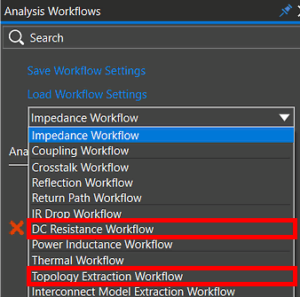 The DC Resistance and Topology Extraction workflows have been added to the IDA workflow list for direct access within System Capture.
The DC Resistance and Topology Extraction workflows have been added to the IDA workflow list for direct access within System Capture. Based on the target IC impedance, estimate and place decoupling capacitors at the schematic stage. A target impedance section is added to the Add Bypass Capacitors and Change Capacitor Quantity windows.
Based on the target IC impedance, estimate and place decoupling capacitors at the schematic stage. A target impedance section is added to the Add Bypass Capacitors and Change Capacitor Quantity windows.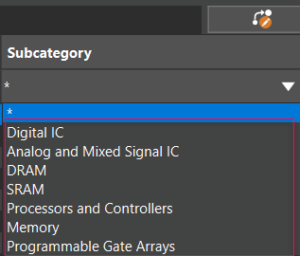 The new subcategories are supported for ICs including Digital IC, Analog and Mixed Signal IC, DRAM, SRAM, Processors and Controllers, Memory, and Programmable Gate Arrays.
The new subcategories are supported for ICs including Digital IC, Analog and Mixed Signal IC, DRAM, SRAM, Processors and Controllers, Memory, and Programmable Gate Arrays.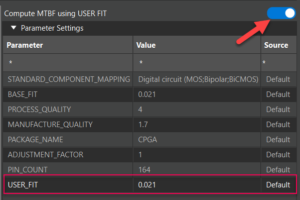 The USER_FIT parameter is now available to calculate MTBF. This parameter is supported for the FIDES standard.
The USER_FIT parameter is now available to calculate MTBF. This parameter is supported for the FIDES standard.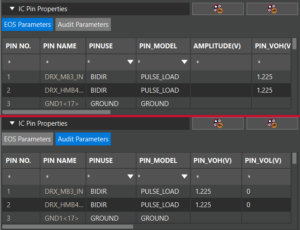 The IC Pin Properties section of the Electrical Stress Settings dialog box now has separate categories for EOS and audit parameters. The EOS parameters now include amplitude (V), pulse width, time period, frequency, and delay.
The IC Pin Properties section of the Electrical Stress Settings dialog box now has separate categories for EOS and audit parameters. The EOS parameters now include amplitude (V), pulse width, time period, frequency, and delay.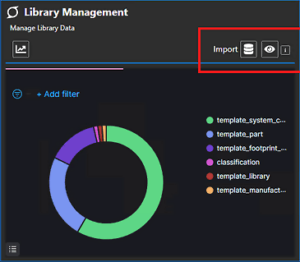 All published data in an Allegro X Managed Library database, including data objects, can be imported into Pulse.
All published data in an Allegro X Managed Library database, including data objects, can be imported into Pulse.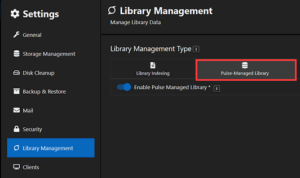 A new solution, Allegro X Managed Library (AML), for centralized library authoring, data management, and enterprise collaboration has been introduced in this release for Allegro System Capture. AML standardizes workflows, ensures data consistency, and streamlines the PCB design process in a scalable environment integrated with Pulse.
A new solution, Allegro X Managed Library (AML), for centralized library authoring, data management, and enterprise collaboration has been introduced in this release for Allegro System Capture. AML standardizes workflows, ensures data consistency, and streamlines the PCB design process in a scalable environment integrated with Pulse.