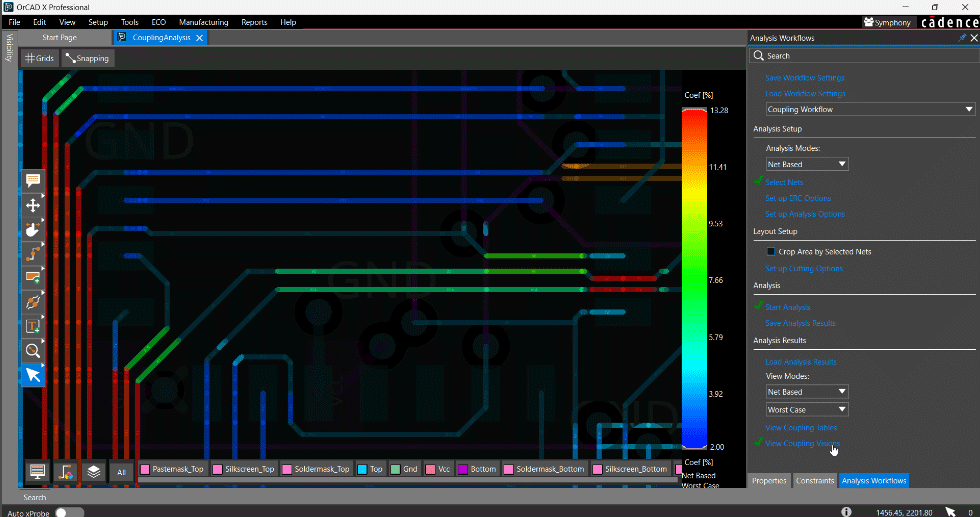
Designing complex printed circuit boards (PCBs) requires powerful and precise electronic design automation (EDA) tools. The choice between leading platforms like Altium Designer and Cadence Allegro often presents difficulty. This article aims to provide a technical comparison, examining the core features, benefits, and considerations for both, discussing the capabilities each brings to the design table in the ongoing “Altium vs Allegro” discussion. Both tools are industry standards, but they cater to slightly different niches and workflows, making a nuanced understanding quite helpful.
Altium vs Allegro X: Feature and Benefit Overview
| Feature Area | Altium Designer | Cadence Allegro X |
| User Interface (UI) | Highly intuitive, visually appealing, and often cited for ease of initial use. | Powerful, offering extensive customization once mastered, rewarding designers with control and flexibility. |
| Constraint Management | Hierarchical rule structure, visual process within a single window. | Spreadsheet-based, set-based approach; robust for complex high-speed rules, reusable constraint sets. |
| High-Speed Design | Capable, with good routing and signal integrity features. | Renowned for advanced high-speed features, signal integrity, and power integrity analysis. |
| Library Management | Intuitive library creation process, integrated component management. | Extensive and diverse component libraries that are highly configurable and available in the cloud or on-premise. |
| Routing Capabilities | Auto-routing and manual routing aids. | Advanced routing technologies (e.g., auto-interactive delay tuning, diff-pair routing). |
| Scalability | Suitable for a broad range of projects, from simple to complex. | The preferred enterprise solution is adept at managing more complex projects. |
| System Resource Use | Generally integrated, it can be resource-intensive for large designs. | Offers both integrated and separate application flows based on preference, often using less RAM during operation. High capacity. |
| Support | Includes support tickets, chat, documentation, and community forums. | 24/7 online support, local phone support, software downloads, articles, community forums, and documentation. |
Cadence Allegro X: Technical Prowess and Advantages
Cadence Allegro X, particularly within the larger Cadence ecosystem, truly shines in its ability to handle the most demanding PCB challenges. It’s often the tool of choice for intricate, high-speed, and high-density designs, seeing its highest use in enterprise-level environments.
Here are some key advantages:
- Superior Constraint Management: Allegro’s constraint management system is a significant differentiator. It employs a powerful spreadsheet-based, group-based, and set-based approach that allows designers to define, manage, and reuse complex rules for signal integrity, timing, physical constraints, and design for manufacturability (DFM) with remarkable precision.
- High-Speed and High-Density Design Expertise: When it comes to signal integrity (SI) and power integrity (PI), Allegro stands out. Allegro provides a suite of tools for advanced SI analysis, comprehensive power distribution network (PDN) design and analysis, and constraint-driven routing that’s beyond useful for high-speed performance. Think about things like impedance control, cross-talk minimization, and precise delay tuning for differential pairs.
- Advanced Routing Technologies: Allegro offers advanced routing features, including auto-interactive delay tuning, pin swapping, and differential pair routing, which are particularly useful for managing intricate signal paths in modern PCBs. This makes it well-suited for high-density interconnect (HDI) designs with microvias and other advanced fabrication techniques.
- Extensive Component Libraries and Ecosystem: With Allegro, designers gain access to an extensive and diverse selection of component libraries.

While some might find Allegro’s initial user interface less “intuitive” than others during the first handful of times using it, its power and efficiency become clear once a user is accustomed to its workflow. This is enterprise-grade software, built for engineers who need granular control and analytical depth.
Allegro’s Suitability for Team Sizes and Workflows
Allegro’s design architecture and comprehensive feature set naturally lend themselves to specific team structures and project scopes. It’s truly built to scale, making it the preferred enterprise solution for managing more complex projects. For large organizations and enterprise environments, the benefits are clear:
- Enterprise Scalability: Allegro’s architecture, which often breaks functions into distinct applications, can be more memory-efficient during multiple operations. This modularity is beneficial for handling extremely large designs with many layers, components, and intricate interconnections without bogging down system resources. This enables teams to tackle monumental projects that would overwhelm lesser platforms.
- Cohesive Team Workflows: Its tight integration within the broader Cadence suite (including OrCAD) creates a cohesive workflow from schematic capture through layout and analysis. This unified ecosystem is valuable for large teams, as it minimizes data translation issues and enhances communication across project phases. Additionally, the unified ecosystem enables scalability between OrCAD and Allegro giving even greater capabilities and flexibility to design teams.
- Standardization and Collaboration: The component libraries and powerful constraint management system are particularly beneficial for large teams. They enable the establishment of standardized design practices and reusable rule sets, which enforce consistency, reduce errors, and accelerate design cycles, particularly when multiple designers work on different sections of a complex board.
Altium Designer: Strengths and Design Considerations
Altium Designer offers a compelling, unified design environment that integrates schematic, PCB layout, and manufacturing outputs into a single platform. It has gathered praise for its user-friendly interface and relatively straightforward learning path.
Here are some of its noteworthy aspects:
- Intuitive User Experience: Many designers find Altium’s UI to be visually appealing and easy to navigate. Its “what you see is what you get” approach means that the design process often feels more direct and less abstract, which can certainly speed up initial design cycles, especially for less complex boards.
- Unified Design Environment: Having everything from schematic capture to PCB layout within one application streamlines the design flow.
- Library Creation and Management: Altium has a relatively fast library creation process. This ease of component management can be a boon for designers who frequently create custom parts or maintain extensive in-house libraries.
- Design Rule Management: Altium features a hierarchical folder structure for organizing design rules, which makes it easier to view and manage these rules at a glance. Creating custom constraint areas with “Room objects” is also straightforward.
However, for very high-end, complex designs with high-speed requirements, designers might find themselves navigating some limitations compared to Allegro’s specialized toolset. While Altium is capable of handling complex boards, the depth of its constraint management for advanced high-speed and/or SI/PI scenarios and the breadth of its routing technologies do not match those of Allegro, which has a dedicated focus on these areas. Additionally, the rule application in Altium can sometimes involve scripting or coding, and its constraint management for reusing specific rule sets across different regions might not be as seamless as Allegro’s method.
Altium vs Allegro: Final Considerations

It can be difficult to choose between Altium vs Allegro, as project scope and team structure come into play. Altium Designer’s intuitive environment may be ideal for individual designers and small teams, just engaged in general-purpose PCB development. Given the complexities of today’s PCB design, particularly in terms of performance, signal integrity, and integration, Cadence Allegro X stands out as a comprehensive solution for advanced engineering challenges. Allegro’s specialized capabilities in areas like constraint management, high-speed routing, and power integrity analysis provide the depth and control essential for innovative development and collaborative, complex engineering workflows. The definitive choice will always align with the unique demands of your design challenges and team operational structure.
EMA Design Automation is a leading provider of the resources that engineers rely on to accelerate innovation. We provide solutions that include PCB design and analysis packages, custom integration software, engineering expertise, and a comprehensive academy of learning and training materials, which enable you to create more efficiently. For more information on Altium vs Allegro and how we can help you or your team innovate faster, contact us.