Company: LumenRadio | Industry: IoT | Solution: OrCAD X, Allegro X
“Cadence is a strong company. You can expand with Cadence, you have lots of tools. It’s a great way forward for us as we are growing—we can just expand what we’re using from Cadence.”
— Niclas Norlén, CTO, LumenRadio
About LumenRadio
LumenRadio is a Swedish technology company focused on advancing wireless communication for the Internet of Things and entertainment lighting industries. Founded with the vision that wireless technology would transform the world, LumenRadio develops innovative platforms that enable reliable wireless connectivity while improving energy efficiency and resource utilization. Their technologies support businesses deploying large-scale IoT networks by delivering high reliability, scalability, and performance.
Goals

LumenRadio set out to build a reliable and scalable IoT platform capable of supporting billions of connected devices. As the IoT ecosystem rapidly expands, the company aimed to deliver wireless hardware that could operate efficiently in crowded RF environments while maintaining strong connectivity and security. Their goal was to create a flexible and intelligent platform, called Mira, that enables businesses to deploy IoT networks quickly while maintaining high performance and reliability.
Challenges
Designing hardware for a large-scale IoT platform presents several technical challenges.
Reliability
With billions of devices relying on the same radio-frequency spectrum, maintaining reliable wireless communication is difficult. LumenRadio needed hardware capable of adapting to constantly changing RF traffic and avoiding interference.
Adaptability
Mira required hardware that is flexible and aware of its surroundings. In order to use the RF spectrum in the most efficient way possible, the design needed to be able to adapt to constantly changing RF traffic at exactly the right time.
Time-to-Market Requirements
Time-to-market was critical as LumenRadio was trying to deploy it’s products as fast as possible to combat the tough economic landscape.
To meet these challenges, the company required design tools that could support complex schematic creation, efficient PCB layout, and rapid development cycles to bring products to market quickly. LumenRadio turned to OrCAD X.
Results
Results “It was really easy to pick up the basics and start my design. I didn’t really need to attend any class. [My previous company] used tools from other competitors, and they were really hard to get started with. I remember I spent days in training just to get started. But OrCAD was easy to get started with, and I could do pretty advanced things with the tools immediately.”
- Niclas Norlén, CTO at LumenRadio
By adopting OrCAD X and Allegro X PCB design tools, LumenRadio was able to streamline its hardware development workflow and achieved a fast time-to-market.
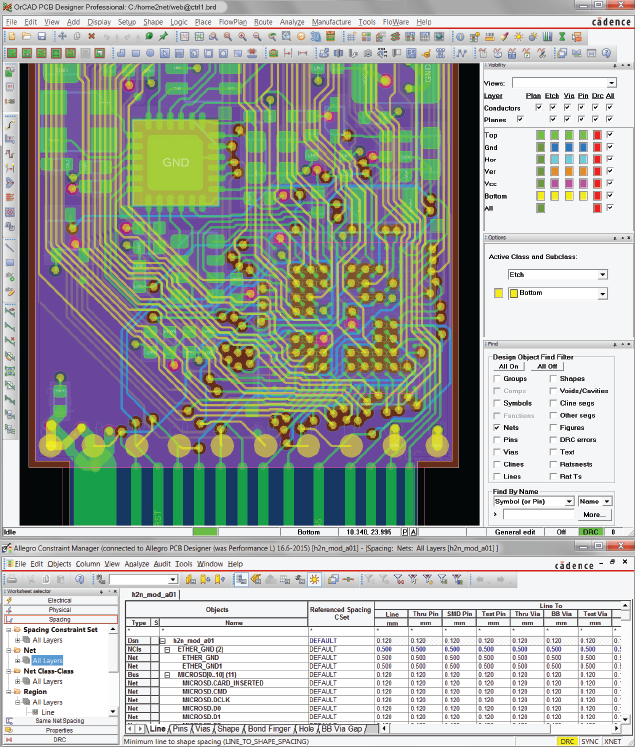
OrCAD X Capture
Engineers quickly captured ideas in OrCAD X Capture and created complex hierarchical schematics while reusing proven circuitry from earlier designs.
OrCAD X and Allegro X PCB
The integration between schematic design and PCB layout enabled faster transitions into physical hardware development. LumenRadio initially outsourced board layout and routing. With a large base of layout experts using OrCAD X and Allegro X, there was a natural draw to this complete ecosystem to support their hardware development.
As a result, LumenRadio significantly reduced design time, improved productivity, and accelerated product delivery—helping the company bring reliable IoT solutions to market more quickly. Learn more about LumenRadio’s success with OrCAD X and Allegro X here.